Infertility can be an emotionally challenging experience for many women and families. When pregnancy does not happen naturally, it often brings confusion, anxiety, and many unanswered questions. Understanding the causes of female infertility explained by a gynecologist helps reduce fear and brings clarity to what can feel like an overwhelming situation.
Female infertility is more common than people realize, and in many cases, it is treatable. Infertility does not mean a woman cannot become a mother—it simply means that the body may need medical support. Many fertility-related conditions develop silently, without obvious symptoms, which is why early awareness and evaluation are important.
A gynecologist plays a key role in identifying fertility concerns and guiding women toward appropriate care. By understanding the medical, hormonal, and lifestyle factors that affect fertility, women can make informed decisions about their reproductive health. This blog explains the most common causes of female infertility in a simple, supportive, and easy-to-understand way.
of female infertility explained by a gynecologist can help reduce fear and bring clarity to the situation.
Female infertility is more common than many people realize, and in most cases, it is treatable with timely medical care. Infertility does not mean the end of motherhood—it simply means the body needs medical support. Many causes of infertility develop silently without obvious symptoms, which is why early evaluation is important.
A gynecologist plays a key role in identifying the underlying reasons for infertility and guiding women toward the right treatment. By understanding what affects fertility, women can take informed steps toward better reproductive health. This blog explains the most common causes of female infertility in a simple, reassuring, and easy-to-understand way.
Ovulation Problems and Irregular Egg Release

Ovulation is a critical part of the fertility process. It occurs when an ovary releases a mature egg that can be fertilized. If ovulation does not happen regularly or properly, pregnancy becomes difficult. Many women with ovulation problems may not notice clear symptoms, making this issue easy to overlook.
Irregular or missed periods are often the first sign that ovulation may not be occurring normally. Causes of ovulation problems include hormonal imbalance, excessive stress, thyroid disorders, sudden weight gain or loss, and certain medical conditions. In some cases, ovulation may happen unpredictably, making it difficult to identify fertile days.
Gynecologists diagnose ovulation issues through blood tests, menstrual tracking, and ultrasound monitoring. Once identified, treatment may include medications to stimulate ovulation, lifestyle changes, or hormonal regulation. The encouraging news is that ovulation-related infertility is one of the most treatable causes. With proper medical guidance and monitoring, many women are able to restore regular ovulation and improve their chances of conceiving naturally.
Hormonal Imbalance and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Hormonal balance is essential for a healthy menstrual cycle and successful conception. When hormones are imbalanced, ovulation may not occur regularly, reducing fertility. One of the most common conditions linked to hormonal imbalance is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS).
Women with PCOS may experience irregular periods, acne, weight changes, excessive hair growth, or difficulty ovulating. Other hormonal issues, such as thyroid disorders or elevated prolactin levels, can also interfere with fertility. These conditions disrupt the natural communication between the brain and ovaries, affecting egg development and release.
Diagnosis involves blood tests, ultrasound imaging, and symptom assessment. Treatment focuses on restoring hormonal balance through medication, weight management, dietary changes, and cycle regulation. Many women with hormonal imbalance or PCOS successfully conceive with timely treatment. Early diagnosis helps prevent long-term complications and makes fertility treatment more effective and less stressful.
Uterine and Fallopian Tube Conditions
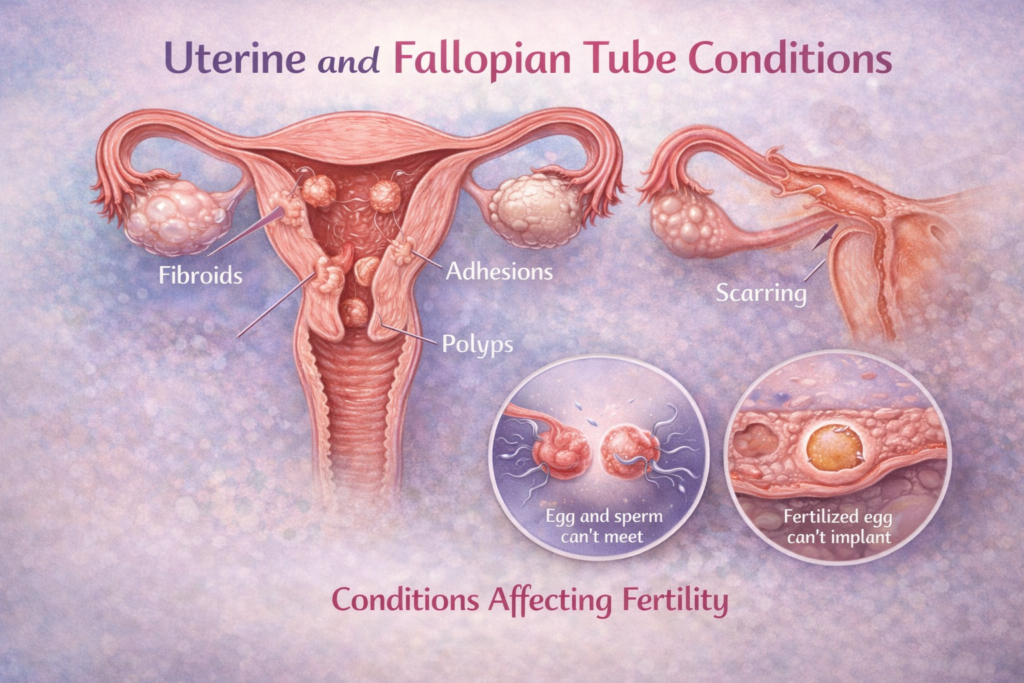
The uterus and fallopian tubes play a vital role in conception and pregnancy. Structural or functional problems in these organs can prevent fertilization or implantation. Blocked fallopian tubes may stop the egg and sperm from meeting, while uterine issues can affect embryo attachment.
Common uterine conditions include fibroids, polyps, scar tissue, or congenital abnormalities. Fallopian tube blockage may occur due to infections, previous surgeries, or inflammation. These issues may not always cause pain or noticeable symptoms, which is why they are often discovered during fertility evaluation.
Gynecologists use ultrasound scans and specialized imaging tests to identify uterine and tubal problems. Many of these conditions are treatable with medication or minor procedures. Early diagnosis improves treatment success and reduces complications. With proper care, many women with uterine or tubal conditions go on to have healthy pregnancies.
Age and Lifestyle Factors Affecting Fertility
Age is a natural factor that influences female fertility. Fertility gradually declines after the age of 30 and more significantly after 35 due to changes in egg quality and quantity. While many women conceive later in life, age-related fertility decline is an important consideration.
Lifestyle habits also play a significant role. Smoking, alcohol use, poor nutrition, lack of physical activity, irregular sleep, and chronic stress can negatively impact reproductive health. These factors may affect hormone levels, ovulation, and overall body balance.
The positive aspect is that lifestyle-related fertility issues can often be improved. Gynecologists encourage healthy eating, regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep to support fertility. Making positive lifestyle changes not only improves the chances of conception but also supports a healthier pregnancy and overall well-being.
Unexplained Infertility and the Need for Ongoing Evaluation
In some cases, fertility tests may appear normal, yet pregnancy does not occur. This condition is known as unexplained infertility. While the term can be frustrating, it does not mean that pregnancy is impossible. It simply indicates that the cause is not immediately visible through routine testing.
Unexplained infertility may involve subtle issues related to egg quality, fertilization, implantation, or timing. Advanced monitoring and continued evaluation can help uncover these factors over time. Sometimes, small adjustments in treatment or lifestyle lead to successful conception.
Gynecologists reassure patients that unexplained infertility is manageable. With patience, medical guidance, and emotional support, many women conceive naturally or with minimal intervention. Understanding that fertility is complex helps reduce self-blame and encourages a hopeful, informed approach.
How Medical Conditions Can Influence Fertility
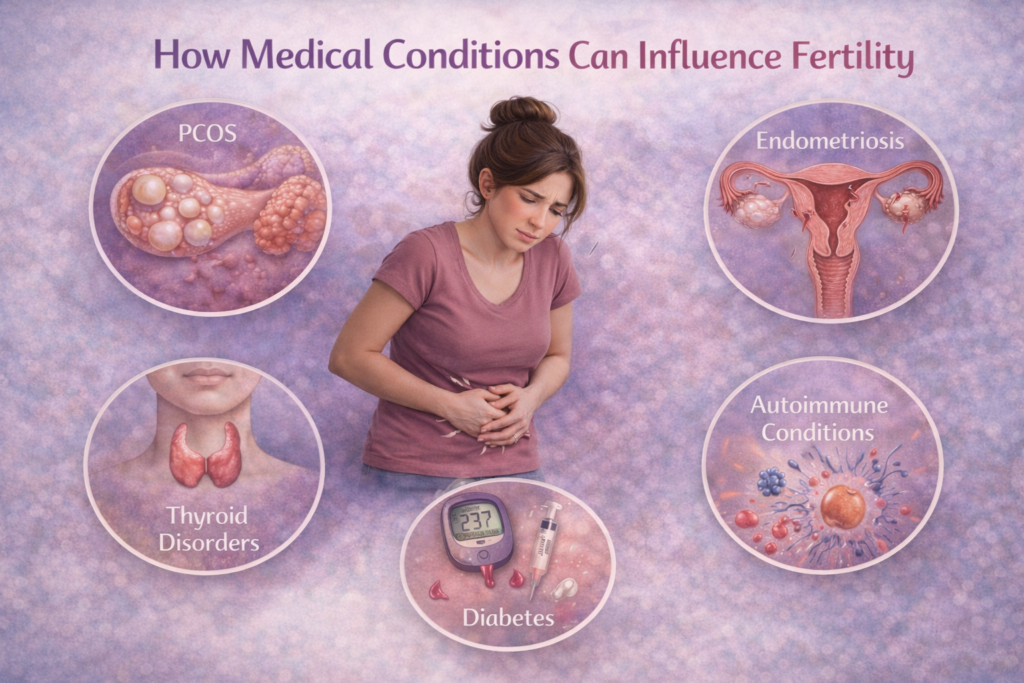
Certain medical conditions can quietly affect a woman’s ability to conceive. Chronic illnesses such as thyroid disorders, diabetes, autoimmune diseases, and hormonal conditions may interfere with normal reproductive function. These conditions can disrupt ovulation, affect egg quality, or create an environment that is not ideal for pregnancy.
For example, thyroid imbalance can cause irregular periods or ovulation problems, while uncontrolled diabetes may impact hormonal balance and implantation. Autoimmune conditions can sometimes affect the uterus or hormonal signaling, making conception more challenging. Many women may not realize that an existing medical condition is contributing to fertility difficulties.
Gynecological evaluation helps identify these underlying health issues and manage them effectively. With proper medical treatment and regular monitoring, fertility outcomes can improve significantly. Managing overall health is an important step in supporting reproductive wellness and preparing the body for pregnancy.
The Role of Body Weight and Nutrition in Fertility
Body weight and nutrition play a vital role in reproductive health. Being underweight or overweight can disrupt hormone levels and ovulation, making conception more difficult. Sudden weight changes may also affect menstrual regularity and egg release.
A balanced diet provides the nutrients needed for hormone production, egg development, and overall reproductive function. Deficiencies in iron, folic acid, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients may negatively affect fertility. Poor eating habits and excessive consumption of processed foods can further impact hormonal balance.
Gynecologists often recommend nutritional improvements as part of fertility care. Small, consistent dietary changes can restore hormonal stability and support ovulation. Maintaining a healthy body weight and nourishing the body properly helps create a favorable environment for conception and supports long-term reproductive health.
Infections and Their Impact on Reproductive Health
Infections of the reproductive tract can affect fertility if not diagnosed and treated early. Conditions such as pelvic inflammatory disease, sexually transmitted infections, or untreated vaginal infections may cause inflammation or scarring that interferes with conception.
Some infections may not produce noticeable symptoms, allowing damage to progress silently. Inflammation can affect the uterus or fallopian tubes, making fertilization or implantation difficult. Early diagnosis through medical evaluation helps prevent long-term complications.
Gynecological care focuses on identifying infections promptly and providing appropriate treatment. Preventive care, regular check-ups, and awareness of symptoms help protect reproductive health. With timely treatment, many infection-related fertility issues can be avoided or reversed.
Why Early Fertility Awareness Makes a Difference

Early awareness of fertility health empowers women to make informed decisions about their reproductive future. Many fertility-related conditions develop gradually and show subtle signs that are often ignored. Understanding menstrual patterns, body changes, and reproductive health indicators allows early action.
Women who seek medical advice early often have more treatment options and better outcomes. Fertility awareness includes knowing when to seek evaluation, understanding risk factors, and making healthy lifestyle choices. Education helps remove myths and misconceptions surrounding fertility.
Gynecologists encourage fertility awareness at every stage of life, not only when pregnancy is planned. Early attention to reproductive health supports long-term wellness and reduces the emotional burden associated with fertility challenges later on.
Conclusion
Understanding the causes of female infertility explained by a gynecologist helps women approach fertility challenges with knowledge and confidence rather than fear. Infertility is a medical condition, not a personal failure, and in most cases, effective treatment options are available.
Early evaluation, lifestyle awareness, and timely medical care play a crucial role in improving reproductive outcomes. With the right guidance and support, many women successfully overcome fertility challenges and move forward with hope. Awareness is the first step toward positive change and better reproductive health.